Nicotine / THR - Statements from Organizations

"Tobacco Harm Reduction = SAFER than smoking"
The items list below may also be found on this Google Doc
Multinational / International
World Health Organization EURO Office
International Agency for Research on Cancer


European Parliament
SCENIHR - European Commission Directorate-General, Health & Consumer Protection


Cochrane systematic evidence review
- Source / 78 scientific studies (including >34 randomized control trials) involving 22,052 participants in a dozen countries.
15 past presidents of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco (SRNT)
- Source NOTE: This is not a statement by the SRNT.


World Heart Federation
The Tobacco Atlas
- Source / Vital Strategies was formed out of a merger between World Lung Foundation and The Union.


Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
European Respiratory Society


Center For Black Equity

Region: England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales
UK Department of Health, Towards a Smokefree Generation - A Tobacco Control Plan for England
Office for Health Improvement & Disparities


Public Health England
Royal College of Physicians


British Medical Association
Cancer Research UK


British Lung Foundation
Asthma + Lung UK


Primary Care Respiratory Society
Roy Castle Lung Cancer Foundation


British Thoracic Society
British Heart Foundation


The British Psychological Society
UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)


Royal College of General Practitioners
Royal Society for Public Health


UK Parliament - Science, Innovation and Technology Committee
Stroke Association


Royal College of Occupational Therapists
Action on Smoking and Health UK (ASH)


National Centre for Smoking Cessation and Training (NCSCT)
Royal college of Psychiatrists


Faculty of Public Health
Royal Pharmaceutical Society


Royal College of Midwives
Chartered Institute of Environmental Health


LGBT Foundation
UK Teratology Information Service


Centre for Mental Health
London Fire Brigade


UK National Fire Chiefs Council
Association of Directors of Public Health North East


Rethink Mental Illness
UK Centre for Tobacco and Alcohol Studies


Royal College of Nursing
Heart UK


Association of Directors of Public Health
College of Mental Health Pharmacy


Fresh North East
Healthier Futures


Mental Health Foundation
Mental Health Nurses Association


London Tobacco Alliance

Mental Health Providers Forum
Stop Smoking London


Public Health Action
North East North Cumbria ICB Smokefree


Smokefree Sheffield
Smokefree Yorkshire & Humber
Hertfordshire County Council

Camden and Islington Public Health

Sheffield Clinical Commissioning Group
Unite in Health
Public Health Nottinghamshire County

Sheffield City Council
Tobacco Control Collaborating Centre
York Mental Health & Addictions Research Group
Sheffield Children’s
Oral Health Foundation
- Source (Formerly known as the British Dental Health Foundation)
Drug Science UK
Men's Health Forum UK
Community Pharmacy Sheffield
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
Zest Community Centre
Sheffield Health and Social Care
diva Sheffield
Scottish Government

Scottish Directors of Public Health
Scottish Health Promotion Managers
National Health Service Scotland
Action on Smoking and Health Scotland
NHS Lothian
NHS Ayrshire and Arran - Scotland

NHS Glasgow and Clyde - Scotland

Scottish Collaboration for Public Health Research and Policy
Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland
NHS Tayside
Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow
Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh
Royal Environmental Health Institute of Scotland
Scottish Consultants in Dental Health
Scottish Thoracic Society
University of Edinburgh
University of Stirling
Health Information and Quality Authority (Ireland)

Irish Cancer Society
The Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development
Irish Heart Foundation
Health and Safety Executive
ASH Ireland
Health Service Executive
Men’s Development Network
Dental Health Foundation - Ireland
Mental Health Ireland
Irish Medical Organisation
Irish Pharmacy Union
Men's Health Forum - Ireland
Public Health Wales

South East Tobacco Control Network
Australia (See Also: "Australia and New Zealand")
Therapeutic Goods Administration (Australia)]

The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners +14 Endorsements

Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (Australia)

Cancer Council - Victoria
- Source
- E-cigarettes may be beneficial for individuals who smoke and use them to quit smoking completely.
- E-cigarette aerosols contain considerably lower amounts of harmful and toxic chemicals compared to conventional cigarette aerosols. An extensive study from 2021 tested carbonyl compounds (including aldehydes such as acetaldehyde and formaldehyde, Section 12.4.3.2) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs, Section 12.4.3.6) levels in e-cigarette compared to conventional cigarette and heated tobacco products aerosols. Among the 19 carbonyl compounds tested, 17 were lowest in e-cigarette aerosols. Among the 22 PAHs that were detected, 21 were lowest in e-cigarette aerosols compared to conventional cigarette and heated tobacco products. When comparing average levels of all the compounds in each class, e-cigarettes had a 99% reduction per puff of carbonyl compounds compared to conventional cigarettes, and a 98% reduction per puff of PAHs, many of which are known causes of cancer.
Australia and New Zealand
Royal Australian & New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP)
- Source
- NOTE: New Statement 2023 (current graphic from old statement) E-cigarettes and vaporisers

Royal Australasian College of Physicians

Drug and Alcohol Nurses of Australasia

Belgium
Belgian Superior Health Council
“Yes, the e-cigarette has its risks, but is clearly less harmful than a traditional tobacco cigarette. According to the Council, the e-cigarette can therefore be a tool to give up tobacco completely.” [Google Translate]
Canada
Government of Canada

Health Canada
“If you are an adult that currently smokes, switching completely to vaping is a less harmful option than continuing to smoke. …Vaping is not known to cause Popcorn lung.” (January 2023) “While vaping products are not harmless, vaping exposes people who smoke to lower levels of harmful chemicals than continuing to smoke.” Statement from Minister of Health (January 16 2023).
Canadian Heart & Stroke Foundation

Centre for Addiction and Mental Health +3 organizations - Canadian Lower-Risk Nicotine Use Guidelines (LRNUG)
“Funded by Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program, the LRNUG has developed several resources to help guide people who use, or are thinking about using nicotine, on how to lower the risk associated with these products. ...E-cigarettes with nicotine may be an effective cessation aid for people who use combustible tobacco. People who switch from combustible tobacco to e-cigarettes will reduce their exposure to numerous toxicants and carcinogens.” Quick Tips: “Using tobacco in forms that don’t burn, like smokeless tobacco or heat-not-burn products, will reduce your exposure to harmful combusted chemicals including carbon monoxide. [You can] further reduce your risk by switching to products that don’t have tobacco like NRT [e.g., nicotine patches or nicotine gum] or e-cigarettes.” Statement by: CAMH - Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Pharmacists for a Smoke-free Canada, The Ontario Tobacco Research Unit, Centre for Effective Practice

Canadian Cancer Society

Canadian Lung Health Foundation
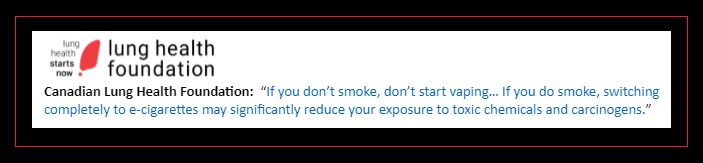
England (See Region: England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales)
France
French National Academy of Medicine

French National Cancer Institute

French High Council for Public Health

French National Academy of Pharmacy

Collège de la médecine générale (College of General Medicine)
“Concerning the electronic cigarette, we consider it as a risk reduction tool and believe that we should not discourage the smoking patient who is learning to vape with a view to weaning [reducing smoking] by indicating to him that it is necessary to avoid the use concomitant cigarette/e-cigarette.”
Germany
German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment

German Society of Addiction (Deutsche Suchtgesellschaft – Dachverband der Suchtfachgesellschaften)
“In general, one can assume that the vapor from an e-cigarette is much less harmful than conventional cigarette smoke and that the e-cigarette can be used for nicotine withdrawal if guideline-based psychotherapeutic and/or drug treatments for nicotine withdrawal are ineffective or unwanted.”
Ireland (See Region: England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales)
Isle of Man
Public Health Isle of Man
“E-cigarettes can be a particularly helpful way to stop smoking tobacco especially when combined with a specialist face to face support. Although experts say they are not entirely risk free, they are at least 95% less harmful than tobacco.”
Luxembourg
Fondation Cancer
“The electronic cigarette … does not contain tobacco. The vapor produced does not contain carbon monoxide or carcinogenic substances in significant quantities. Despite a lack of long-term scientific studies, it probably presents a reduced risk compared to tobacco (if not combined with cigarettes). …In general, we recommend that you vape with the most concentrated liquid possible, in order to reduce your consumption of liquid and therefore your exposure to inhaled substances.” [emphasis in original] [Google Translate]
Malaysia
Federation of Private Medical Practitioners' Associations, Malaysia

New Zealand (See Also: "Australia and New Zealand")
New Zealand Ministry of Health

Official New Zealand Ministry of Health Position Statement
“Vaping is not harmless but it is much less harmful than smoking. Vaping has the potential to help people quit smoking and contribute to New Zealand’s Smokefree 2025 goal.” Organizations that support this statement include: Health Promotion Agency/Te Hiringa Hauora (HPA), Hāpai te Hauora/Māori Public Health, New Zealand Medical Association (NZMA), Action for Smokefree 2025 (ASH), National Training Service (NTS), All District Health Boards, Pharmacy Guild of New Zealand, New Zealand Heart Foundation, New Zealand College of Midwives, Parents Care Centre
New Zealand Medical Association

New Zealand Pharmacy Council

Cancer Society of New Zealand

New Zealand Heart Foundation

Asthma & Respiratory Foundation NZ


Quitline NZ

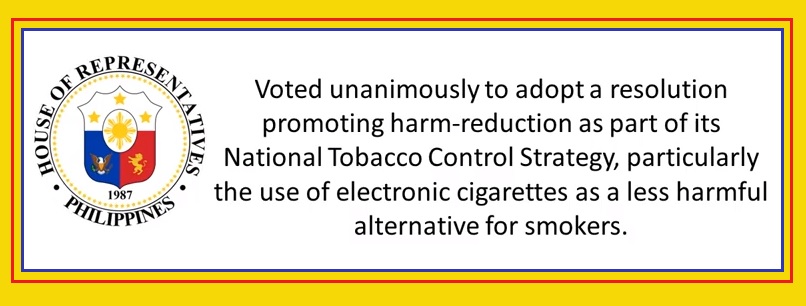
Philippines
House of Representatives Philippines
2018
Poland
2023: Polish Psychiatric Association
Scotland (See Region: England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales)
United Kingdom (See Region: England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales)
United States
Center for Critical Public Health

American Association of Public Health Physicians

American College of Preventive Medicine

American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery

American Society of Addiction Medicine

Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration

US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine

US Food & Drug Administration #1 #2 #3

National Institute on Drug Abuse

US Centers for Disease Control

Truth Initiative

Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids (CTFK)

American Association for Cancer Research and American Society of Clinical Oncology

American Cancer Society

American Heart Association

Eau Claire, WI Health Department
2022

Uruguay
Uruguayan Council of Ministries
2021

Wales (See Multinational pt. 2/United Kingdom)
Important! Instructions to page editors:
1 meme for each org, with a link saved on wayback machine of the source so anyone can verify it was said.
Updated information e.g. better quotes to use may be left in the suggestions section below:
Suggestions to add to this page
Tobacco Tactics - University of Bath
British Society of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry
2023: Association of Directors of Public Health North East Position Statement on Nicotine Vaping September 2023
- Many European authorities, such as the German Federal Risk Assessment Institute and the
Federal Centre for Health Education in Germany, the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (Netherlands), and the UK Committees of Toxicity, Mutagenicity, and Carcinogenicity of Chemicals in Food, Consumer Products, and the Environment, focused on the importance of e-cigarettes and heated tobacco as a safe alternative compared to burning cigarettes.
2023: Page 3 of this email from FDA screenshot included below, as well as PDF of the full mail (preserving blue links to the FDA website)


